Authentication | Web Application
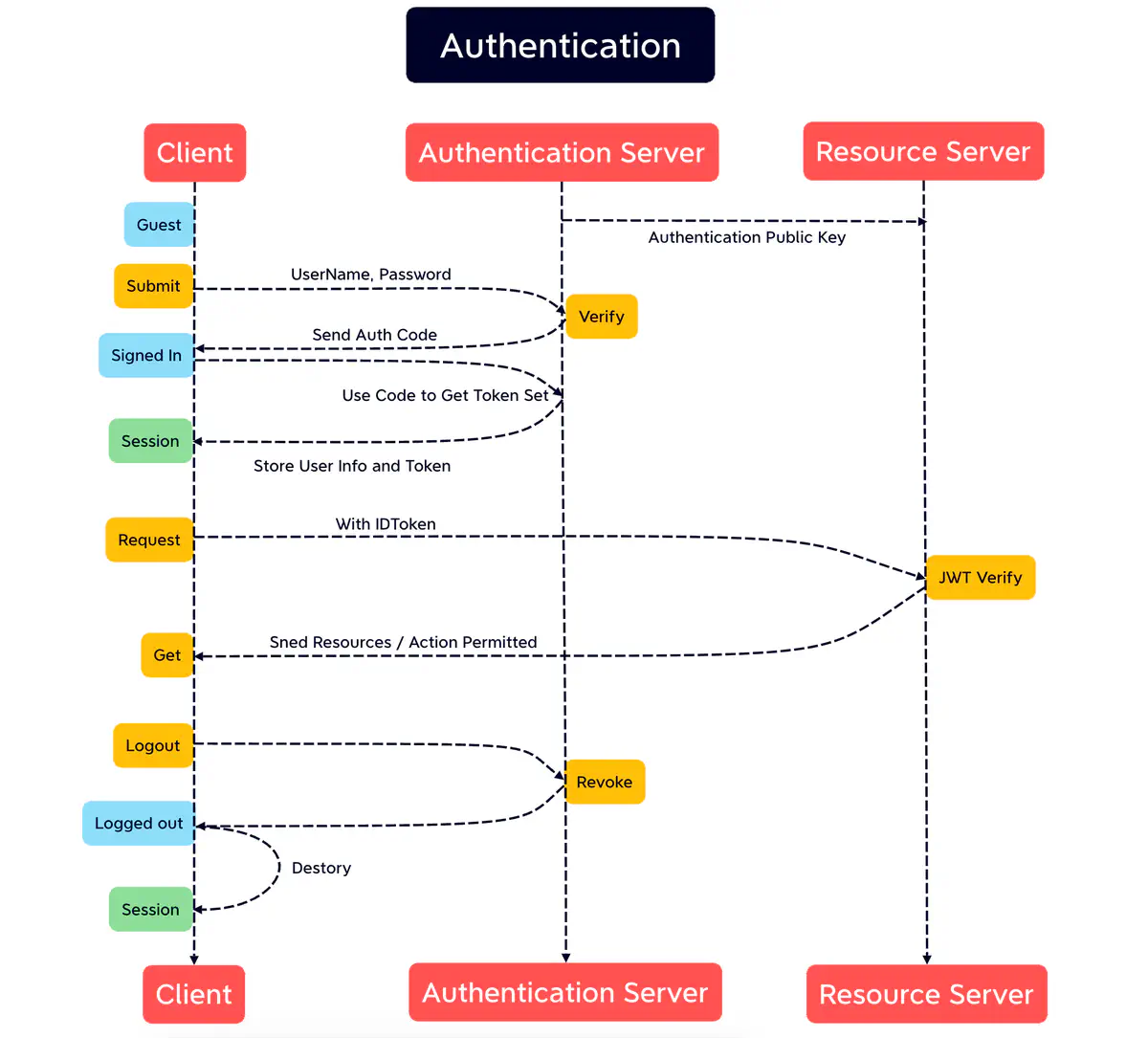
Authentication Flow
- A User sends Username/Password Authentication Request
- The Authentication Server verifies Username/Password against the Database
- The Authentication Server returns JWT Token after validation successfully
- The Client stores JWT Token in Session
- The Client sends Request to Resource Server and presents idToken in the Request
- The Resource Server verifies JWT Token using public AuthToken from the Authentication Server and returns resources to the valid User
- The Authentication Server revokes the JWT Token and the client logs out
Authentication Token
ID Tokens are for authentication: They tell you who someone is.
Access Tokens are for authorization: They tell you what someone is allowed to do.
Refresh Tokens allow for extended access to resources by obtaining fresh access tokens without repeated user interactions.
📚 ID Token:
Purpose: Used to identify the user.
Content: Contains claims about the user’s identity. For example, the user’s name, email, and more.
Protocol: Associated mainly with OpenID Connect (OIDC), which is a layer built on top of OAuth 2.0 specifically for authentication.
Usage: Typically used by the client to get user details after authentication.
📚 Access Token:
Purpose: Used to access protected resources.
Content: Contains information about the scopes and permissions granted to the client. It doesn’t necessarily contain information about the user.
Protocol: OAuth 2.0.
Usage: Sent to the resource server (API) to authorize access to protected resources. Access tokens have a short lifespan for security reasons.
📚 Refresh Token:
Purpose: Used to obtain new access tokens.
Content: Does not contain information about permissions or user details. It’s a long-lived token, allowing the application to request a new access token without requiring the user to log in again.
Protocol: OAuth 2.0.
Usage: If an access token expires and the application still needs to access the user’s protected resources, it can present the refresh token to the authorization server. If valid, the server issues a new access token (and potentially a new refresh token).